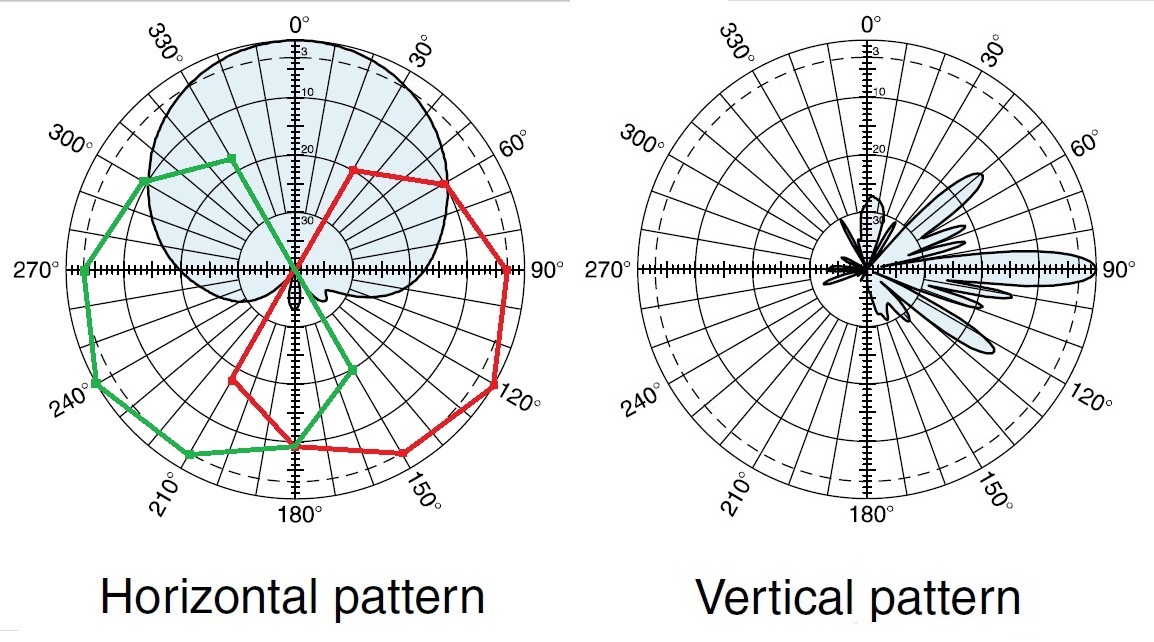
Web the antenna feed points would be in series with the loop, such that a small loop looks somewhat like a short circuit across the antenna feed. The radiated power is now maximum along the axis of the loop, not in the plane of the loop. Web let’s start with a simple square loop in free space, fed in the middle of one side, and see how the radiation pattern and other characteristics vary as we change the frequency (or change the length in wavelengths, which is the same thing). The tangent line at 0° indicates vertical polarization, whereas the line with 90° indicates horizontal polarization. Web loop antennas are usually classified as electrically small ( c < λ / 3 ) and electrically large (c ∼ λ ).
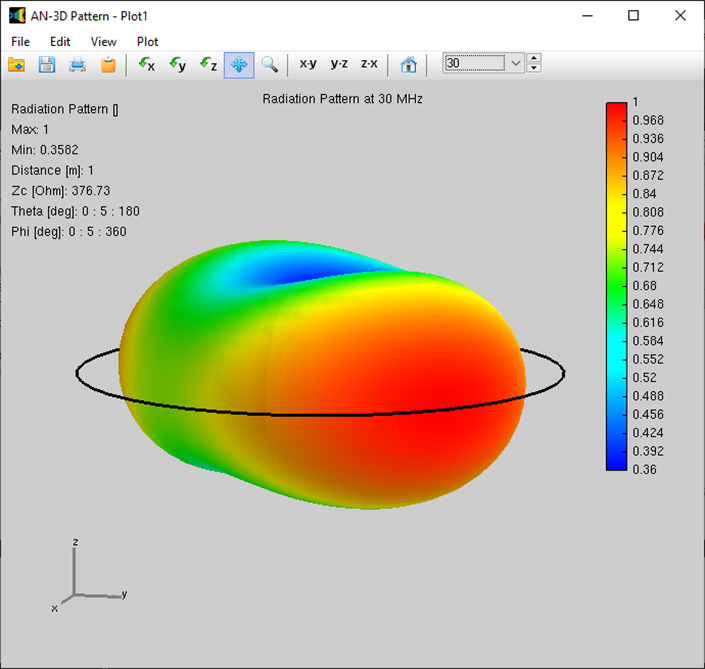
As the frequency progresses to the second and third resonances the perpendicular radiation fades and strong lobes near the plane of the loop arise. The pattern is similar to a dipole, but about 6 degrees wider however, the vertical pattern is more compressed, providing about 1 db of gain. Web an antenna is a device that couples currents to electromagnetic waves for purposes of radiation or reception. These antennas have low radiation resistance and high inductive reactance, so that their impedance is difficult to match to a radio impedance (often 50 ohms). The radiation patterns for different angles of looping are also illustrated clearly in the figure.
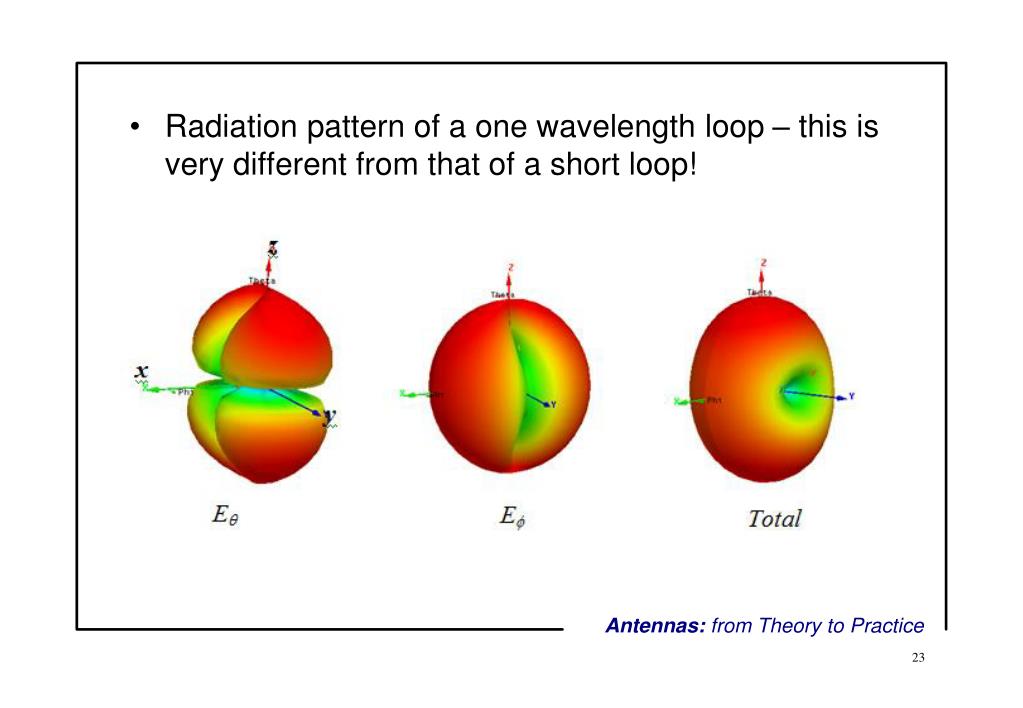
The tangent line at 0° indicates vertical polarization, whereas the line with 90° indicates horizontal polarization. Web a radiation pattern defines the variation of the power radiated by an antenna as a function of the direction away from the antenna. Web let’s start with a simple square loop in free space, fed in the middle of one side, and see how the radiation pattern and other characteristics vary as we change the frequency (or change the length in wavelengths, which is the same thing). As the frequency progresses to the second and third resonances the perpendicular radiation fades and strong lobes near the plane of the loop arise. The radiation patterns for different angles of looping are also illustrated clearly in the figure.
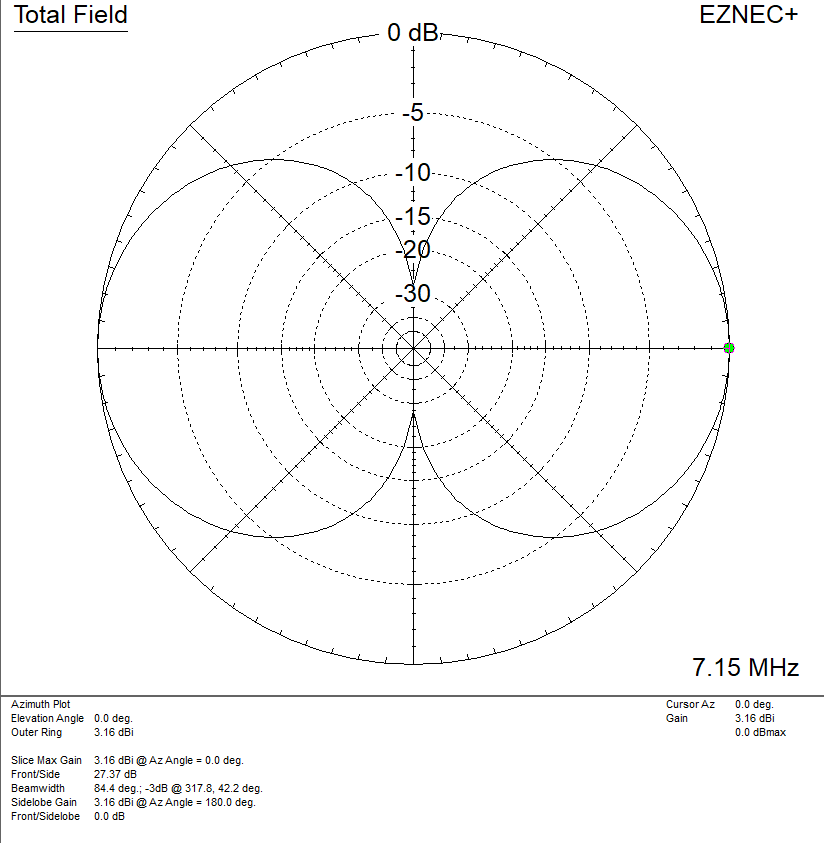
Web a radiation pattern defines the variation of the power radiated by an antenna as a function of the direction away from the antenna. Web loop antennas are usually classified as electrically small ( c < λ / 3 ) and electrically large (c ∼ λ ). Web an antenna is a device that couples currents to electromagnetic waves for purposes of radiation or reception. This still qualifies as a “small loop”, but is beginning to show some of the characteristics of a larger loop. Web let’s start with a simple square loop in free space, fed in the middle of one side, and see how the radiation pattern and other characteristics vary as we change the frequency (or change the length in wavelengths, which is the same thing). The tangent line at 0° indicates vertical polarization, whereas the line with 90° indicates horizontal polarization. Radius of loop= 5.3 mm, circumference = λ. As the frequency progresses to the second and third resonances the perpendicular radiation fades and strong lobes near the plane of the loop arise. Here, c denotes the loop’s circumference. The pattern is similar to a dipole, but about 6 degrees wider however, the vertical pattern is more compressed, providing about 1 db of gain. Web azimuth radiation pattern of a horizontally polarized full wave loop antenna in free space. This power variation as a function of the arrival angle is observed in the antenna's far field. These antennas have low radiation resistance and high inductive reactance, so that their impedance is difficult to match to a radio impedance (often 50 ohms). The small loops of a single turn have small radiation resistance (< 1 ω) usually comparable to their loss resistance. Courtesy himanshu rohilla, 3rd year ee, iit delhi.
The Small Loops Of A Single Turn Have Small Radiation Resistance (< 1 Ω) Usually Comparable To Their Loss Resistance.
Web a radiation pattern defines the variation of the power radiated by an antenna as a function of the direction away from the antenna. Web the antenna feed points would be in series with the loop, such that a small loop looks somewhat like a short circuit across the antenna feed. Here, c denotes the loop’s circumference. As the frequency progresses to the second and third resonances the perpendicular radiation fades and strong lobes near the plane of the loop arise.
The Radiation Patterns For Different Angles Of Looping Are Also Illustrated Clearly In The Figure.
Courtesy himanshu rohilla, 3rd year ee, iit delhi. Web loop antennas are usually classified as electrically small ( c < λ / 3 ) and electrically large (c ∼ λ ). This power variation as a function of the arrival angle is observed in the antenna's far field. Web let’s start with a simple square loop in free space, fed in the middle of one side, and see how the radiation pattern and other characteristics vary as we change the frequency (or change the length in wavelengths, which is the same thing).
The Pattern Is Similar To A Dipole, But About 6 Degrees Wider However, The Vertical Pattern Is More Compressed, Providing About 1 Db Of Gain.
This still qualifies as a “small loop”, but is beginning to show some of the characteristics of a larger loop. Web an antenna is a device that couples currents to electromagnetic waves for purposes of radiation or reception. The radiated power is now maximum along the axis of the loop, not in the plane of the loop. Radius of loop= 5.3 mm, circumference = λ.
The Tangent Line At 0° Indicates Vertical Polarization, Whereas The Line With 90° Indicates Horizontal Polarization.
Web azimuth radiation pattern of a horizontally polarized full wave loop antenna in free space. These antennas have low radiation resistance and high inductive reactance, so that their impedance is difficult to match to a radio impedance (often 50 ohms).