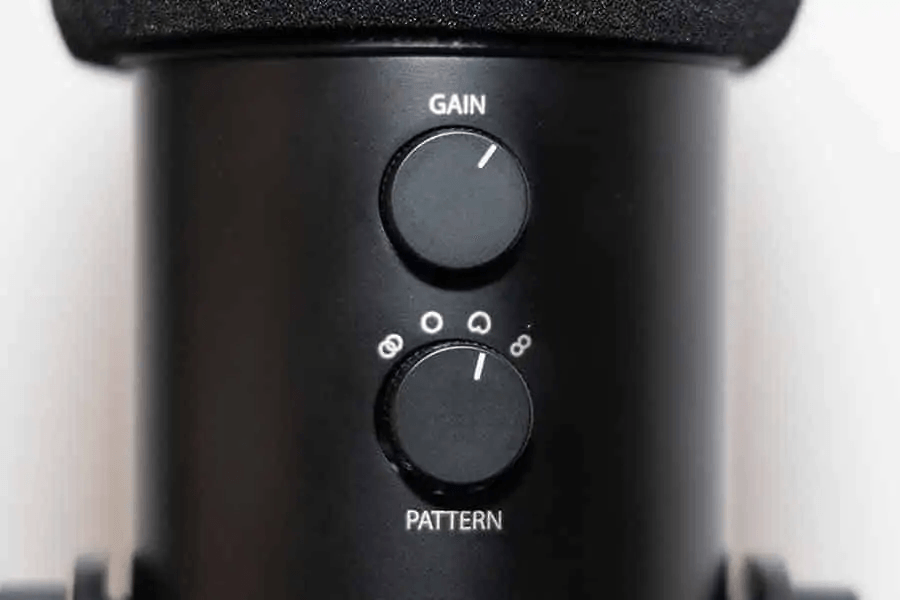
This means you have to configure it properly to pick up an acceptable amount of noise. Web the yeti microphone settings for picking up sound include four patterns that can be interchanged. When it comes down to it, this setting blocks out any unwanted sound. Setting up the blue yeti. Gain, simply put, is the level of allowed sound input to the microphone.
Web the yeti microphone settings for picking up sound include four patterns that can be interchanged. The blue yeti’s 4 modes and adjusting the gain settings. Web the four polar patterns (or modes) offered by the blue yeti microphone are: The indicator will be vertical if gain is centered. As a condenser microphone, the blue yeti has a frequency response of 20hz to 20khz, which is sensitive enough to pick up even the faintest sound in the surroundings.
The blue yeti offers four recording patterns: Check the settings in your recording software / daw. Web in order to prevent any keyboard feedback or loud mouse clicking coming through to the microphone, you can adjust your blue yeti settings accordingly. Reduce the gain to low without muting the microphone completely. Setting the gain to zero or at its lowest level reduces the microphone’s sensitivity.
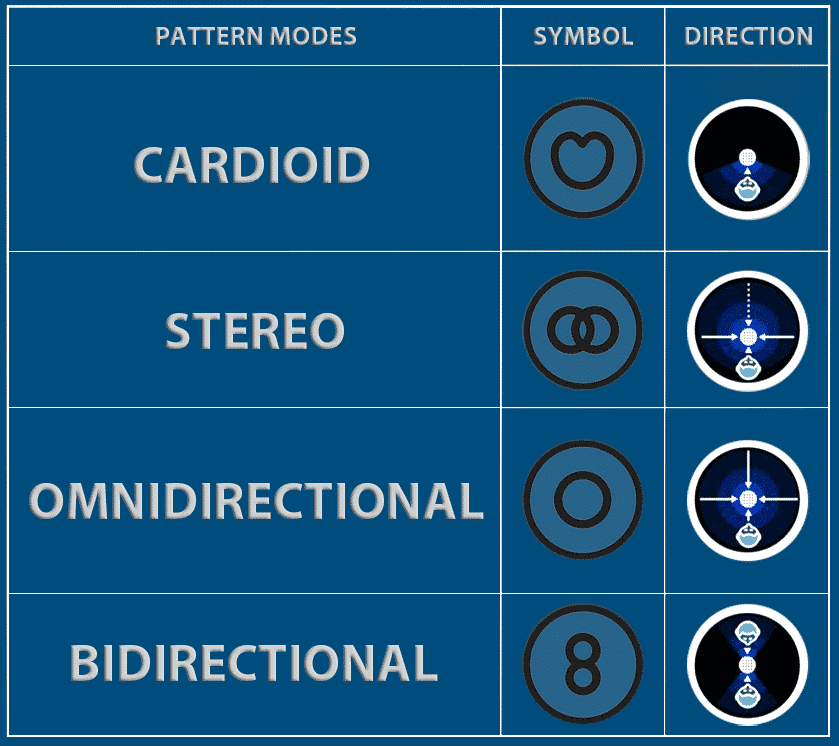
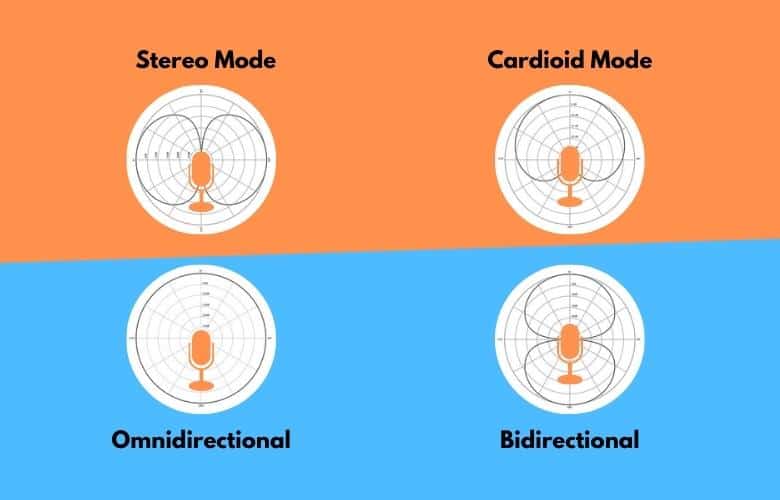
Understand the difference between mic gain and volume. Gain can be adjusted via the central knob on the backside of the microphone and should be centered to start. Web so, to access these settings you need to go to start → change system sounds → recording → blue yeti mic → properties. Choose the appropriate pickup pattern. Place the mic about 10 in (25.4 cm) away from your mouth. The blue yeti offers four recording patterns: This is ideal for recording loud sound sources or when the microphone is close to the audio source. Check the settings in your recording software / daw. Web zero gain or low gain: Web the four blue yeti microphone patterns or modes are bidirectional, cardioid, omnidirectional, and stereo. Web in this video i show you the blue yeti pickup patterns that your microphone can be set to in order to achieve the ideal recording setup for your podcast. Web the four polar patterns (or modes) offered by the blue yeti microphone are: The polar pattern is the area on the microphone that is sensitive to audio signals. To choose the best blue yeti settings adjust two things. Use a shock mount / boom arm.
The Indicator Will Be Vertical If Gain Is Centered.
Web but don’t worry, you can transform your blue yeti audio from lousy to legendary by changing your blue yeti settings. On the yeti microphone, the cardioid mode is seen as the best mode. Reduce the gain to low without muting the microphone completely. Web polar patterns are settings that determine how the mic picks up all of the sounds around it.
The Gain Setting Controls How Sensitive The Microphone Is, And If It’s Set Too High, It Can Cause Problems With Feedback And Noise.
Web the four polar pattern settings available in the blue yeti microphone are cardioid, stereo, omnidirectional, and bidirectional. It helps prevent distortion and clipping in situations where the input level is naturally high. Choose the appropriate pickup pattern. Web so, to access these settings you need to go to start → change system sounds → recording → blue yeti mic → properties.
Each Pattern Serves A Specific Purpose, Allowing You To Tailor Your Microphone’s.
Everything you need to know to get clear audio for your blue yeti microphone. Each blue yeti pattern changes the microphone’s direction of maximum sensitivity and the direction or directions of maximum sound rejection. Web the yeti offers four different pattern settings, so you can choose the one that best suits your needs. The blue yeti offers four recording patterns:
Use A Shock Mount / Boom Arm.
Setting up the blue yeti. But in general, choosing a cardioid pickup pattern, setting the gain to an appropriate level, using a pop filter, and having a strategic microphone placement. Place the mic about 10 in (25.4 cm) away from your mouth. The graph shows the symbols representing each yeti mic mode, their purpose, and how the sound is picked up.
![Best Settings For Blue Yeti Microphone [Expert Guide]](https://www.becomesingers.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/Blue-Yeti-Pattern-Settings.png)