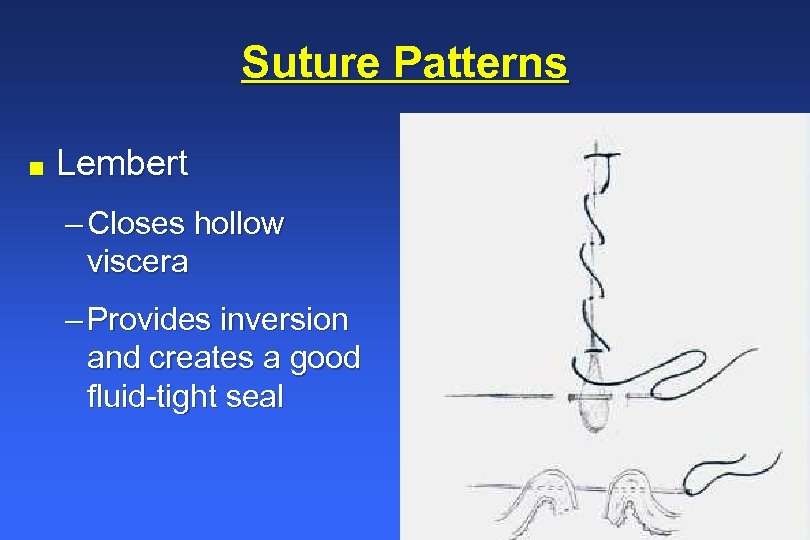
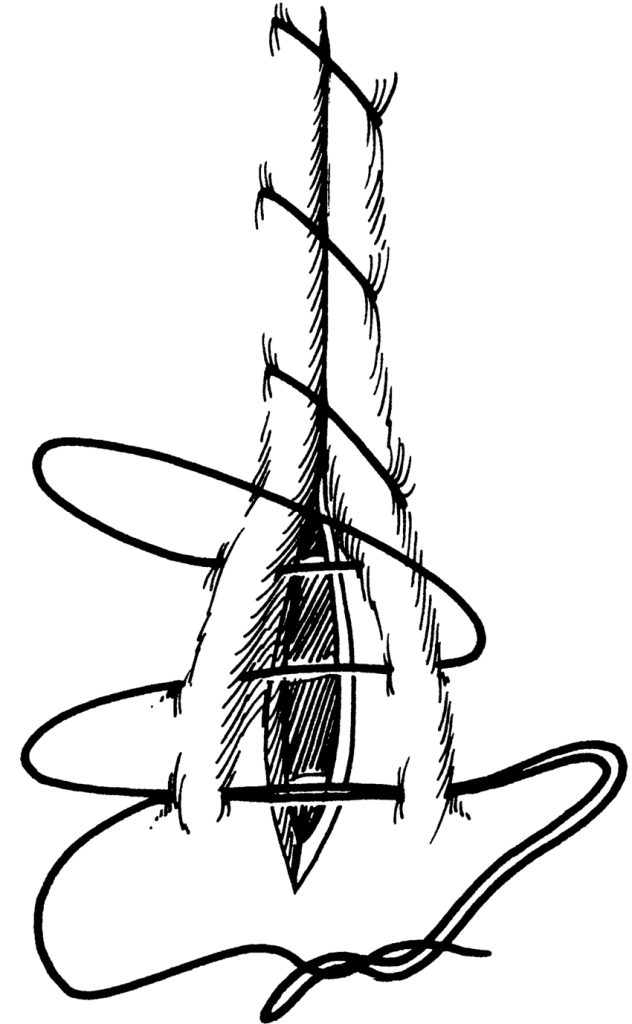
As well as being able to perform the basic patterns, it important to be familiar with their basic properties so you will be able to decide when their use is appropriate. Web surgical techniques in reptiles can be challenging, due to the wide variety of unique anatomic and physiologic characteristics. Web an inverting pattern can sometimes be quite useful, for example to invaginate a section of stomach wall when managing a patient with gastric dilatation and volvulus whose gastric mucosal viability is questionable. Any inverting pattern can be used (lembert, utrecht, cushing). Web start the pexy by placing a suture (#2 pds or nylon) across the caudal aspect of the dorsal sheath.
Two inverting suture lines (cushing or lembert) what layers to include? To create a water tight seal, secure the rumen to the skin using a continuous cushing pattern of 2. These are used to close lumens in large animal species (intestines, bladders, uteri). Web surgical techniques in reptiles can be challenging, due to the wide variety of unique anatomic and physiologic characteristics. Web an inverting pattern can sometimes be quite useful, for example to invaginate a section of stomach wall when managing a patient with gastric dilatation and volvulus whose gastric mucosal viability is questionable.
Suture patterns can be broadly categorized as interrupted or continuous. Web this can be via use of a rumen board, rumen protector or by creating a water tight seal by use of an inverting suture pattern. Patients that have had a diaphragmatic incision will require diaphragmatic closure and removal of intrathoracic air by transdiaphragmatic thoracocentesis or the placement of a chest tube. Web one layer is often described in the literature but that suture line becomes loose as the uterus contracts, making a second advisable. Suture patterns can be broadly categorized as interrupted or continuous.
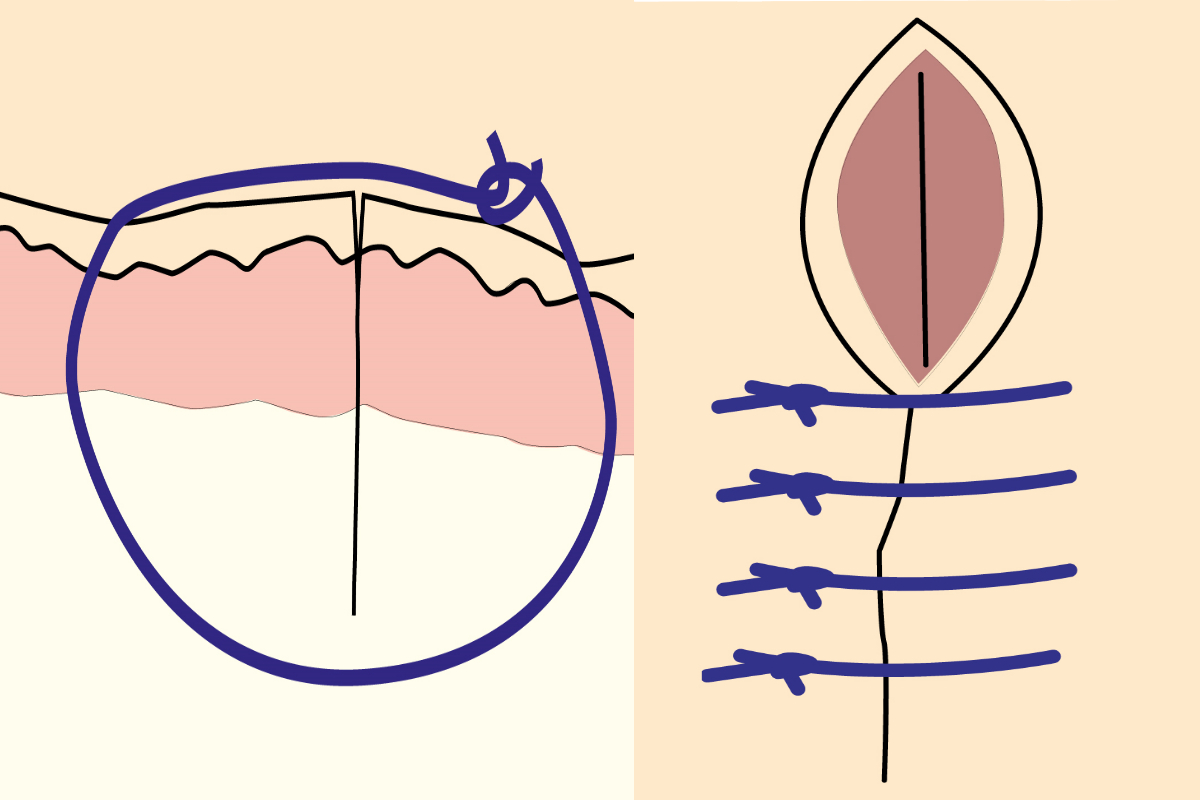
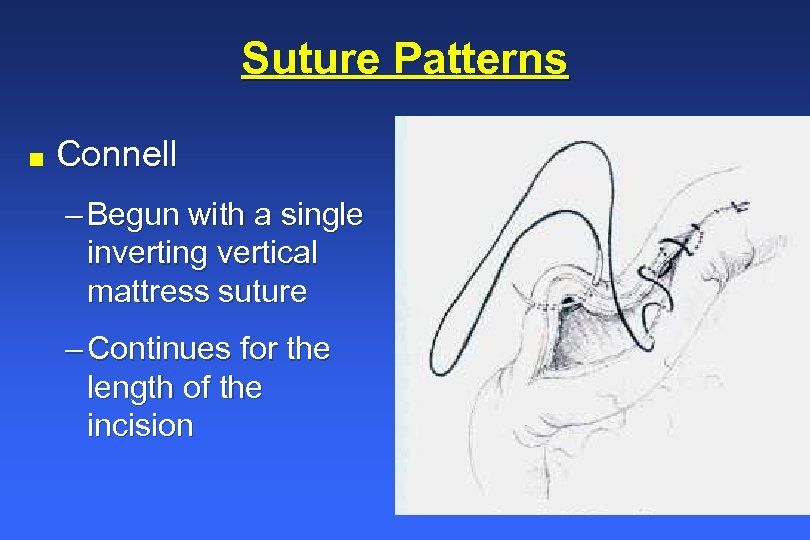
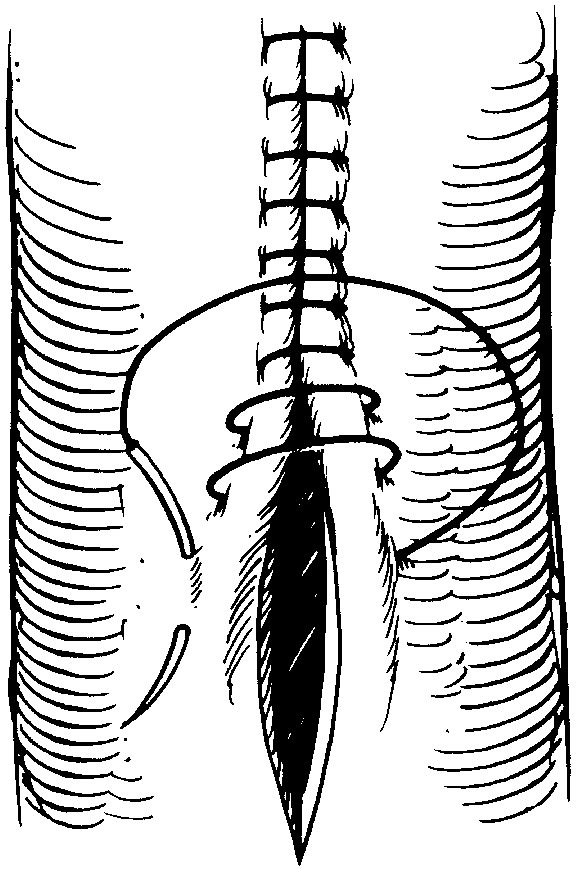
It penetrates the submucosa but does not penetrate the organ’s lumen. Web cushing suture pattern: Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Web using an inverting suture pattern means that the sutures will turn some of the tissue inward. Web this can be via use of a rumen board, rumen protector or by creating a water tight seal by use of an inverting suture pattern. Web this pattern inverts the tissues. The latter is the most effective. Perhaps the most vital component of the correct suture pattern is the surgical knot. Fast, continuous, easy inverting suture technique for intestinal incision bites are taken parallel to the incision but the suture doesn’t pass right through the wall. Web surgical techniques in reptiles can be challenging, due to the wide variety of unique anatomic and physiologic characteristics. A bite is taken symmetrically at an equal distance from either side of the wound and pulled tight. These patterns prevent leakage and minimize the risk of adhesions due to exposed suture. Secure the bite with a knot. Web inverting versus everting suture patterns disrupted tissue may be apposed using a suture pattern that inverts or everts tissues, depending on the wound’s location.
Suture Patterns Can Be Broadly Categorized As Interrupted Or Continuous.
The video demonstrates the steps and tips for creating a secure and effective suture line. There is no need to include the abomasum in this bite. If done correctly, this pattern should invert the tissues enough to cover the first layer leaving only the knots of the inverting pattern visible. Patients that have had a diaphragmatic incision will require diaphragmatic closure and removal of intrathoracic air by transdiaphragmatic thoracocentesis or the placement of a chest tube.
Close The Dorsal Sheath Using A Simple Continuous Pattern.
Absorbable #2 with a swedged on needle is advised. This could, for example, be fecal matter, which could cause a lot of havoc within the abdomen. Web the use of a specific suture pattern may vary depending on the area being sutured, the length of the incision, the tension at the suture line, and the specific need for apposition, inversion, or eversion of the tissues. Web this pattern inverts the tissues.
Web Inverting Patterns Turn The Cut Edges Inward And Minimize Exposed Suture.
Web inverting versus everting suture patterns disrupted tissue may be apposed using a suture pattern that inverts or everts tissues, depending on the wound’s location. Perhaps the most vital component of the correct suture pattern is the surgical knot. 45 most reptiles lack a diaphragm and have a single coelom, intracoelomic testes, a common cloaca, and so forth. Web the continuous cushing pattern is often used for closing incisions in hollow viscera such as the stomach, urinary bladder and uterus.
Web One Layer Is Often Described In The Literature But That Suture Line Becomes Loose As The Uterus Contracts, Making A Second Advisable.
Web start the pexy by placing a suture (#2 pds or nylon) across the caudal aspect of the dorsal sheath. A bite is taken symmetrically at an equal distance from either side of the wound and pulled tight. Suture patterns can be broadly categorized as interrupted or continuous. First layer can be just mucosa and submucosa leaving the muscularis and serosa for the 2 nd layer.