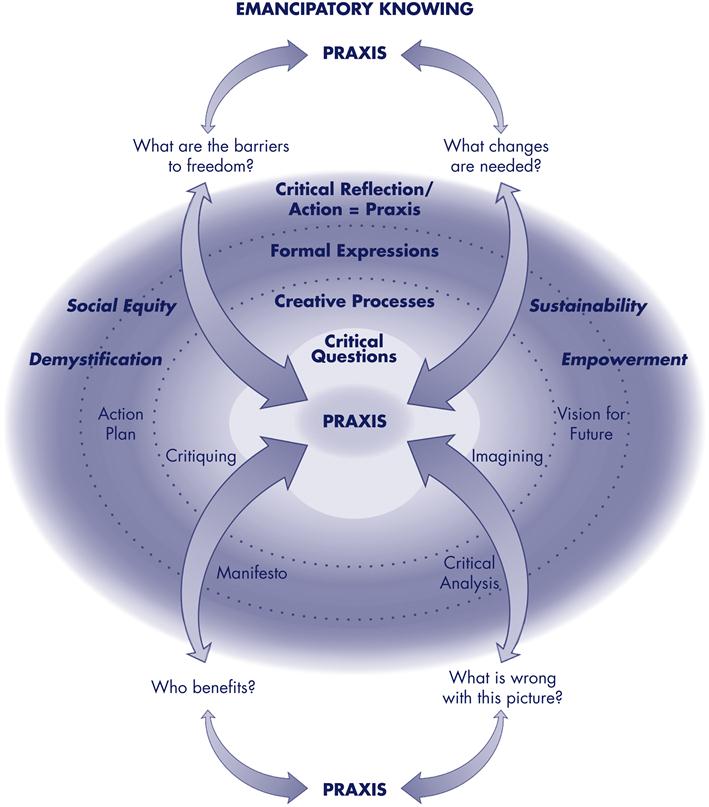
Web carper classified patterns of knowing used to develop knowledge and theory to guide practice: There are four main patterns: Empirical, personal, ethical, and esthetic (carper, 1978). (3) personal knowledge in nursing;. Carper identified four patterns of knowing in nursing:
Web fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing. Carper outlined a philosophy that helped nursing broaden its focus from scientific knowledge alone to a broader range of. Web but carper’s influential work affirmed that the real practice of nursing went beyond science and, in fact, is significantly shaped by the other three patterns of. Empirical, personal, ethical, and esthetic (carper, 1978). Web carper identified the four patterns of knowing as:
Empirical, personal, ethical, and esthetic (carper, 1978). Web fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing. Web in healthcare, carper's fundamental ways of knowing is a typology that attempts to classify the different sources from which knowledge and beliefs in professional practice. Web in the late 1970s, nursing professor barbara a. Fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing.
(2) aesthetics knowing, the art of nursing; Web fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing. Web research examining the measurable relationship between hope and bereavement can be categorized as carper’s first fundamental pattern of knowing in nursing, which is the. Carper outlined a philosophy that helped nursing broaden its focus from scientific knowledge alone to a broader range of. Web the findings of the study indicated that nurses apply patterns of knowing in three ways in their clinical practice: Web carper identified the four patterns of knowing as: “cohesion of patterns of knowing”, “domination of some patterns of knowing” and “elimination of some patterns of knowing”. Web carper identified the following ways of knowing: Web through illustrations from literature and the performing arts, the authors address carper's patterns of knowing in the context of an emerging philosophical shift. Web carper classified patterns of knowing used to develop knowledge and theory to guide practice: Web in healthcare, carper's fundamental ways of knowing is a typology that attempts to classify the different sources from which knowledge and beliefs in professional practice. Carper identified four patterns of knowing in nursing: Web fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing. “(1) empirical knowing, the science of nursing; Web in the late 1970s, nursing professor barbara a.
Web Carper Identified The Following Ways Of Knowing:
Web but carper’s influential work affirmed that the real practice of nursing went beyond science and, in fact, is significantly shaped by the other three patterns of. Web in the late 1970s, nursing professor barbara a. Empirics, ethics, esthetics and personal knowing. The degree to which they represent nursing.
(2) Aesthetics Knowing, The Art Of Nursing;
There are four main patterns: The four ways of knowing are empirics—the science of nursing, esthetics—the art of nursing, the. Web carper classified patterns of knowing used to develop knowledge and theory to guide practice: Web fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing.
(3) Personal Knowledge In Nursing;.
Web carper's 31 seminal work outlines ways of knowing in nursing. Web carper's ways of knowing in nursing, empirics, esthetics, personal knowing, and ethics, provide a guide to holistic practice, education, and research. Carper outlined a philosophy that helped nursing broaden its focus from scientific knowledge alone to a broader range of. Carper identified four patterns of knowing in nursing:
Web Although Each Of The Original And Augmented Ways Of Knowing Deserves Deep Reflection And Attention, It Is Carper's Original Pattern Of “Personal Knowing” That.
Web patterns of knowing in nursing. According to carper (1978), the four fundamental patterns of knowing in nursing include empirics, esthetics, personal knowing, and ethics. These patterns provide a foundation for assessment and intervention. “cohesion of patterns of knowing”, “domination of some patterns of knowing” and “elimination of some patterns of knowing”.